Introduction
HQS Qorrelator App is a user-friendly solution designed to calculate correlation functions using quantum computers.
Correlation functions, and the response spectra that can be calculated from them, are the vital connection between the macroscopic and the microscopic world in physics and chemistry. For example, in chemistry spectroscopy and most importantly Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-spectroscopy is an irreplaceable tool to identify chemical compounds. In physics correlation functions of materials (for example the Green's function) determine how a material responds to external drives like electric fields or currents and are the standard object of interest for almost all work on quantum models like the Hubbard model.
The calculation of correlation functions is one of the earliest use cases where a quantum advantage can be expected. It is based on implementing a quantum time evolution on a quantum computer and sampling from the result. It is vital for users that need to work with correlation functions and response spectra to understand when quantum computers have matured enough to provide a quantum advantage for their use case and how that quantum advantage can be utilized.
The HQS Qorrelator App is designed to provide users with a simple tool to perform the calculation of correlation functions on a quantum computer without being experts in quantum computing. It can be used to benchmark correlation function calculations on current quantum hardware and the potential performance of error corrected quantum computers by using simulators.
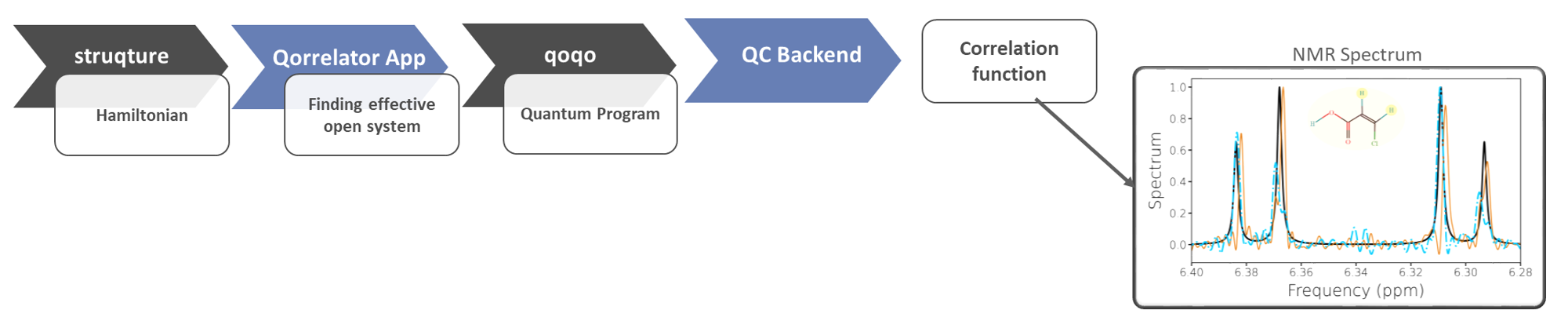
Applications
The first version of the HQS Qorrelator App focuses on calculating the NMR correlation functions on a quantum computer. We focus on NMR for two reasons:
- It is hard to overstate the relevance of NMR in experimentally identifying the molecules present in chemical samples and the number of applications of NMR in industry. It is a commercially highly relevant application.
- In the case of standard NMR it is effectively possible to calculate the correlation function in the infinite temperature limit. In this limit the calculation of a correlation function on a quantum computer simplifies further and is essentially reduced to applying the correct time evolution. This makes NMR an excellent candidate for achieving a quantum advantage.
The NMR spectral function can be obtained from the correlation functions of two spin operators, with respect to the Hamiltonian of the nuclear spins targeted by the NMR measurement. The Qorrelator App will take a description of the Hamiltonian and of the quantum device the calculation should run on as an input. It will return a QuantumProgram a collection of quantum circuits and measurement postprocessing needed to calculate the correlation function with a quantum computer. This QuantumProgram can be run on one of several backends and return the correlation function. The spectral function can be obtained from the correlation function with a simple Fourier transform.
In the near future, all available quantum computers will be NISQ quantum computers, where the qubits of the quantum computer experience environmental noise. In most applications, environmental noise is purely a source of errors. At HQS, we have realized that, for certain applications, environmental noise is not detrimental and can even be used as a computational resource.
The HQS Qorrelator App also incorporates these approaches in a user-friendly manner, by providing an easy way to obtain an estimate of the spectral broadening due to the effective time evolution that occurs on a noisy quantum computer.
Getting started
The following command can be used to install the package via hqstage the HQS tool for managing our proprietary software:
hqstage install hqs_qorrelator_app
The usage section breaks down how the HQS Qorrelator App works together with the HQS struqture and qoqo libraries. We go through the Python interface of the package and discuss how to construct quantum programs that will calculate correlations, how to get an estimated broadening based on the noise in a device and how to extract the noisy algorithm model.
The following code snippet provides a basic example. For more details see
# Import tools
import numpy as np
from qoqo import devices
from qoqo_quest import Backend
from struqture_py import spins
from hqs_qorrelator_app import NMRCorrelator
# Creating a Quantum device the calculation should run on
device = devices.AllToAllDevice(
number_qubits,
["RotateZ", "RotateX", "RotateY", "PauliX", "Hadamard", "SingleQubitGate"],
["CNOT", "Qsim", "SWAP"],
1.0,
)
device = device.add_depolarising_all(1e-5)
# Constructing the NMR hamiltonian
hamiltonian = spins.PauliHamiltonian()
# Shifting the second spin by energy 1
hamiltonian.set("1Z", 1)
# Adding a small ZZ interaction between spins
hamiltonian.set("0Z1Z", 1e-3)
# Creating the QuantumProgram
nmr = NMRCorrelator()
program = nmr.spectrum_program_fixed_step(
hamiltonian, trotter_timestep=0.1, gyromagnetic_factors=[1,1], device=device
)
# Evaluate the program for the correlator after 2 Trotter steps
backend = Backend(number_qubits=2)
res = program.run(backend, [2])
print("Correlation after two trotter steps", res["correlator_total_re"])
Features
The HQS Qorrelator App has the following features:
- Construct a QuantumProgram specific for NMR.
- Construct a QuantumProgram for measuring correlators in infinite temperature environment.
- Create a noise algorithm model for time evolution in correlator measurement.
- Extract the infinite temperature fidelity from a noise model (how well noise model fits infinite temperature assumption).
- Full Python interface.
For experts in quantum computing more features are available when manually constructing quantum programs using the HQS Quantum Libraries.
API Documentation
Changelog
For a changelog starting from version 0.2 please see here.